
IST-2000-28062
Home
Background
Objectives
Results
The System
Project Activities
Deliverables
Consortium
Contact
The System
The AWAKE system will consist of the following components:
A Hypovigilance Diagnosis Module (HDM)
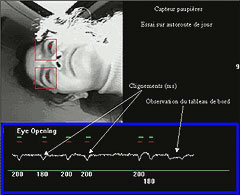
will detect and diagnose driver hypo-vigilance in real-time. Based on an artificial intelligence algorithm this module will fuse data from on- board driver monitoring sensors (eyelid behaviour and steering grip forces) and data regarding the driver’s behaviour (lane keeping performance). The goal is to achieve a (correct) diagnosis level of 90% and a false alarm rate below 1 % in all highway scenarios.
Therefore, parts of the HDM are personalised by using a smart card application. If the driver is unknown to the system it will monitor awake driving at the beginning of the trip and use the information for delivering its diagnoses later on.
The HDM comprises different subsystems which produce independent diagnoses. The final diagnosis will then be fused and has three levels:
- Driver is awake
- Driver may be drowsy
- Driver is drowsy
A Traffic Risk Estimation module (TRE)
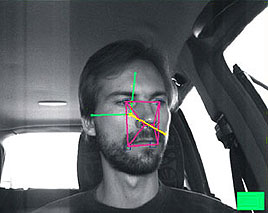
will assess the traffic situation and the involved risks. It will match data from an enhanced digital navigational map, a positioning system, an anti-collision radar, the odometer, and a driver’s gaze direction sensor. The output of this module will be used by the HDM to reassess the state of the driver, and by the Driver Warning System to determine the adequate level of warning.
The HDM comprises different subsystems which produce independent diagnoses. The final diagnosis will then be fused and has three levels:
The TRE diagnosis contains
- a general traffic risk level
- specific traffic risks
- Specific traffic risks are further divided into
- lane departure (left/right),
- frontal collision (cautionary and
- imminent case),
- inadequate speed before
- sharp curves (cautionary and
- imminent case)
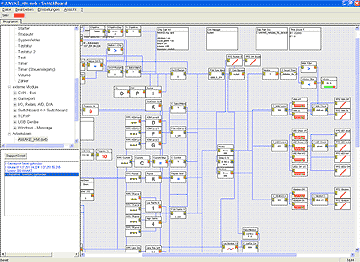
A Hierarchical Manager (HM)
co-ordinates the other system components and hosts the AWAKE warning strategy. The HM uses input from the HDM and the TRE to determine the adequate warning strategy for a certain situation. In addition, information from the smart card is used to personalise the various warnings of the AWAKE system.
According to the diagnosis from the HDM and the TRE the AWAKE warning strategy is as follows:
- If driver is awake, only imminent collision and imminent speed warnings
- can be activated
- If driver may be drowsy, all levels of TRE warnings can be activated
- If driver is drowsy,
- – Two different drowsiness warnings (according to actual traffic risk)
- can be activated
- – In case of specific traffic risks TRE warnings have priority
A Driver Warning System (DWS)
will use acoustic, visual and haptic means according to the type of AWAKE warning.
- Acoustic warnings include different warning tones to raise driver’s alertness
- and speech messages to indicate why the warning has been activated.
- Visual elements of the alarm are either located at the rear view mirror
- for the demo cars or at an external box on top of the dashboard of the truck
- demonstrator. These devices also host the smart card reader and the
- On/Off button of the system.
- The haptic warning is based on a vibration device attached to the seat belt
- lock. The vibrations stimulus can be felt all along the seat belt.



AWAKE HMI for luxury and city cars (left) and heavy vehicles (middle). For the acoustic output onboard loudspeakers are used. The vibration device is mounted at the seatbelt lock (right).